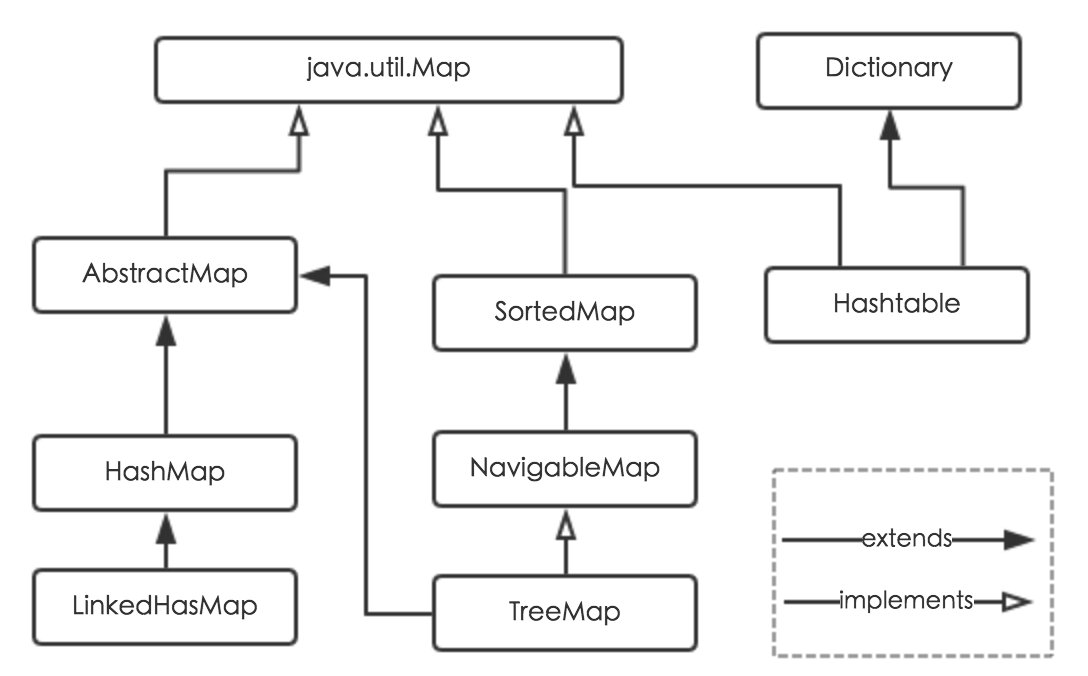
继承及实现关系图
源码注释及翻译
Hash table based implementation of the Map interface. This implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits null values and the null key. (The HashMap class is roughly equivalent to Hashtable, except that it is unsynchronized and permits nulls.) This class makes no guarantees as to the order of the map; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant over time.
基于哈希表的Map接口实现。此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许null值和null键。 (HashMap类大致相当于Hashtable,除了它是不同步的,并且允许null值。)这个类不保证映射的顺序;尤其不保证排序在一段时间内保持不变。
This implementation provides constant-time performance for the basic operations (get and put), assuming the hash function disperses the elements properly among the buckets. Iteration over collection views requires time proportional to the "capacity" of the HashMap instance (the number of buckets) plus its size (the number of key-value mappings). Thus, it's very important not to set the initial capacity too high (or the load factor too low) if iteration performance is important.
假设哈希函数在桶之间正确地分散元素,这个实现为基本操作(get和put)提供了恒定的时间性能。对集合视图的迭代需要与HashMap实例的“容量”(桶的数量)加上其大小(键-值映射数)成正比的时间。因此,如果迭代性能很重要,则不要将初始容量设置得太高(或负载因子太低)是非常重要的。
An instance of HashMap has two parameters that affect its performance: initial capacity and load factor. The capacity is the number of buckets in the hash table, and the initial capacity is simply the capacity at the time the hash table is created. The load factor is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to get before its capacity is automatically increased. When the number of entries in the hash table exceeds the product of the load factor and the current capacity, the hash table is rehashed (that is, internal data structures are rebuilt) so that the hash table has approximately twice the number of buckets.
HashMap的一个实例有两个影响其性能的参数:初始容量和负载因子load factor。容量是哈希表中的桶数bucket,初始容量只是创建哈希表时的容量。负载因子是在自动增加容量之前允许哈希表获取的完整程度的度量。当哈希表中的条目数超过加载因子和当前容量的乘积时,哈希表将被重新哈希(即重建内部数据结构),使得哈希表扩容至两倍的桶数。
As a general rule, the default load factor (.75) offers a good tradeoff between time and space costs. Higher values decrease the space overhead but increase the lookup cost (reflected in most of the operations of the HashMap class, including get and put). The expected number of entries in the map and its load factor should be taken into account when setting its initial capacity, so as to minimize the number of rehash operations. If the initial capacity is greater than the maximum number of entries divided by the load factor, no rehash operations will ever occur.
作为一般规则,默认负载因子(0.75)提供了时间和空间成本之间的良好折中。较高的值会降低空间开销,但会增加查找成本(反映在HashMap类的大多数操作中,包括get和put)。在设置其初始容量时,应考虑映射中的预期条目数及其负载因子,以便最小化重新散列操作的数量。如果初始容量大于最大条目数除以负载因子,则不会发生重新加载操作。
If many mappings are to be stored in a HashMap instance, creating it with a sufficiently large capacity will allow the mappings to be stored more efficiently than letting it perform automatic rehashing as needed to grow the table. Note that using many keys with the same {@code hashCode()} is a sure way to slow down performance of any hash table. To ameliorate impact, when keys are {@link Comparable}, this class may use comparison order among keys to help break ties.
如果要将多个映射存储在HashMap实例中,则创建足够大初始容量的映射将比自动重新散列来扩展表更高效。请注意,使用具有相同hashCode()的多个键将会降低哈希表性能。为了改善影响,当键为Comparable时,此类可以使用比较顺序的键来帮助打破关系。
Note that this implementation is not synchronized. If multiple threads access a hash map concurrently, and at least one of the threads modifies the map structurally, it must be synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation that adds or deletes one or more mappings; merely changing the value associated with a key that an instance already contains is not a structural modification.) This is typically accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the map.
请注意,此实现不同步。如果多个线程同时访问哈希映射,并且至少有一个线程在结构上修改了映射,那么它必须在外部进行同步。(结构修改是添加或删除一个或多个映射的任何操作;仅更改与实例已包含的键关联的值不是结构修改。)这通常通过同步自然封装映射的某个对象来实现。
If no such object exists, the map should be "wrapped" using the {@link Collections#synchronizedMap Collections.synchronizedMap} method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental unsynchronized access to the map:
Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));
如果不存在此类对象,则应使用Collections.synchronizedMap方法“包装”映射。这最好在创建时完成,以防止意外地访问map不同步:
Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));
The iterators returned by all of this class's "collection view methods" are fail-fast: if the map is structurally modified at any time after the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator's own remove method, the iterator will throw a {@link ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined time in the future.
所有这个类的“集合视图方法”返回的迭代器都是'fail-fast':如果在创建迭代器之后的任何时候对映射进行结构修改,除了通过迭代器自己的remove方法之外,迭代器将抛出一个ConcurrentModificationException。因此,面对并发修改,迭代器将干净且快速地失败,而不是在将来不确定时间冒着各种不确定性行为的风险。
Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators throw ConcurrentModificationException on a best-effort basis. Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this exception for its correctness: the fail-fast behavior of iterators should be used only to detect bugs.
请注意,迭代器的“快速失败”行为无法保证,因为一般来说,在不同步并发修改的情况下,它无法做出任何硬性保证。'fail-fast'迭代器会尽最大努力抛出ConcurrentModificationException。因此,不能编写依赖于此异常的程序以确保其正确性,迭代器的快速失败行为应该仅用于检测错误。
注释:fail-fast 机制,即快速失败机制,是java集合(Collection)中的一种错误检测机制。当在迭代集合的过程中该集合在结构上发生改变的时候,就有可能会发生fail-fast,即抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。fail-fast机制并不保证在不同步的修改下一定会抛出异常,它只是尽最大努力去抛出,所以这种机制一般仅用于检测bug。
默认属性
//默认初始容量1<<4,位运算,2的4次方,即16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 还蛮嘻哈的
//最大容量,2的30次方
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
//默认负载因子,0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
//一个桶的树化阈值,当桶中元素个数超过这个值时,需要使用红黑树节点替换链表节点
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
//一个树的链表还原阈值,当扩容时,桶中元素个数小于这个值,就会把树形的桶元素还原(切分)为链表结构
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
//当哈希表中的容量大于这个值时,表中的桶才能进行树形化
//否则桶内元素太多时会扩容,而不是树形化
//为了避免进行扩容、树形化选择的冲突,这个值不能小于 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
默认初始容量16,负载因子0.75,即容量超过16 * 0.75 = 12 时发生rehash扩容至32。